Please switch off AdBlock for this webside to display it correctly (there are no ads here).
Gauss-Lorentz peak
modelname
Gauss-Lorentz|GL
Complex dielectric function is described by four parameters like Voigt broadened peak \(N_1, E_1, B_1, L_1\):
$$
\hat\varepsilon = (1-L_1) \hat\varepsilon_{\rm G} + L_1 \hat\varepsilon_{\rm L}
$$
where imaginary part of dielectric function of Gaussian and Lorentzian peak is parametrized by two ways. First combines peaks wit the same FWHM:
$$
\varepsilon_\mathrm{i,G} = \frac{N_1}{\sqrt{\pi} b B_1 E_1 } \left[ \exp\left(-\frac{4\log(2)(E-E_1)^2}{B_1^2}\right) - \exp\left(-\frac{4\log(2)(E+E_1)^2}{B_1^2}\right) \right]
$$
$$
\varepsilon_\mathrm{i,L} = \frac{b B_1}{\pi E_1} \left[ \frac{1}{(E-E_1)^2 + B_1^2/4} - \frac{1}{(E+E_1)^2 + B_1^2/4} \right]
$$
or alternatively combines peaks with the same curvatures in maxims:
$$
\varepsilon_\mathrm{i,G} = \frac{N_1}{\sqrt{\pi} b B_1 E_1 } \left[ \exp\left(-\frac{(E-E_1)^2}{(b B_1)^2}\right) - \exp\left(-\frac{(E+E_1)^2}{(b B_1)^2}\right) \right]
$$
$$
\varepsilon_\mathrm{i,L} = \frac{b B_1}{\pi E_1} \left[ \frac{1}{(E-E_1)^2 + (b B_1)^2} - \frac{1}{(E+E_1)^2 + (b B_1)^2} \right]
$$
where \(b\) ensuring constant broadening of peak (\(B_1\) is FWHM):
$$
b= \frac{L_1}{2}+\frac{1- L_1}{2 \sqrt{\ln2}} + \sum_{j=1}^4 a_j L_1^j (1- L_1)
$$
\(a_1=0.0552077\), \(a_2=0.0435994\), \(a_3=0.0187772\), \(a_4=0.051632\).
attributes
-
number_of_terms - Adds peaks and corresponding parameters.
-
Asymmetric|A - Add parameters \(M2, \dots\) defining asymmetrical peaks (number of peaks must be higher than 1). Appropriate for modelling of coupled phonon peaks.
-
Fano|F - Add parameters \(M1, \dots\) defining asymmetrical peaks. Appropriate for modelling of Fano resonace between phonon and free carriers.
-
ph - Units 1/cm are used for peak energies \(E_1, \dots\) and broadening parameters \(B_1, \dots\).
-
Head|H - Uses alternative calculation.
Example
media:
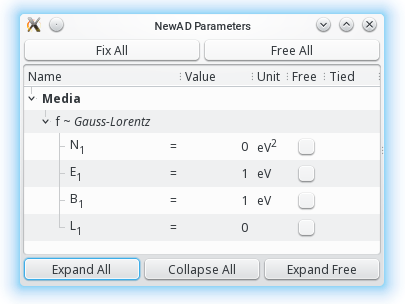
f = Gauss-Lorentz
newAD2> par
N1f = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
E1f = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
B1f = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
L1f = 0 fixed [0,1]
newAD2>

 |
|