Please switch off AdBlock for this webside to display it correctly (there are no ads here).
Classical Drude-Lorentz model (damping harmonic oscillator)
modelname
Lorentz|LBP|Drude|DHO
Complex dielectric function is described by three parameters \(N_1, E_1, B_1\):
$$
\varepsilon = 1 + \frac{2}{\pi} \frac{N_1}{E_1^2 - E^2 - {\rm i} B_1 E} \,,
$$
where parameter \(E1\) is energy corresponding to central frequency.
First alternative model name is
LBP (Lorentzian Broadened Peak):
$$
\varepsilon = 1 + \frac{2}{\pi} \frac{N_1}{E_1^2 + B_1^2/4 - E^2 - {\rm i} B_1 E} \,.
$$
In this case model represents Lorentzian broadened dielectric response of discrete excitations, where parameter \(E1\) corresponds resonant frequency
:
$$
\varepsilon_\mathrm{i} = \frac{N_1 B_1}{2 \pi E_1} \left( \frac{1}{(E_1-E)^2 + B_1^2/4} - \frac{1}{(E_1+E)^2 + B_1^2/4} \right) \,.
$$
Second alternative model name is
Drude. In this case only paramters \(N_1, B_1\) are generated
and model is calculated as follows:
$$
\varepsilon = 1 - \frac{2}{\pi} \frac{N_1}{E^2 + {\rm i} B_1 E} \,.
$$
Third alternative model name is
DHO. In this case the model represents \(m\) coupled dumped harmonic oscillators and dielectric function is calculated as follows:
$$
\hat \varepsilon(E) = 1 + \frac{2}{\pi} \vec N^{\rm T} [\tilde S - E^2 \tilde I - {\rm i} E \tilde B ]^{-1} \vec N \,,
$$
where \(\vec N\) is vector:
$$
\vec N^{\rm T} = (\sqrt{N_1},\sqrt{N_2},\ldots,\sqrt{N_m}) \,,
$$
\(\tilde S\) is diagonal matrix
$$
\tilde S = \left(
\begin{array}{cccc}
E_1^2 & 0 & \cdots & 0 \\
0 & E_2^2 & \cdots & 0 \\
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
0 & 0 &\cdots & E_m^2
\end{array}
\right) \,,
$$
\(\tilde I\) is unit matrix and \(\tilde B\) is symmetric matrix
$$
\tilde B = \left(
\begin{array}{cccc}
B_1 & B_{12} & \cdots & B_{1m} \\
B_{12} & B_2 & \cdots & B_{2m} \\
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
B_{1m} & B_{2m} &\cdots & B_m
\end{array}
\right) \,.
$$
Note that for \(m=1\) this option is equivalent to option
Lorentz.
attributes
-
number_of_terms - Adds terms (peaks) and corresponding parameters.
-
Asymmetric|A -
Add parameters \(M_2, \dots\) defining asymmetrical peaks (requires LBP model and number of peaks must be higher than 1).
Appropriate for modelling of coupled phonon peaks like DHO model but with less number of parameters.
-
Fano|F -
Add parameters \(M_1, \dots\) defining asymmetrical peaks (requires LBP model). Appropriate for modelling of Fano resonace between phonon and free carriers.
-
ph - Units 1/cm are used for peak energies \(E_1, \dots\) and broadening parameters \(B_1, \dots\).
Example
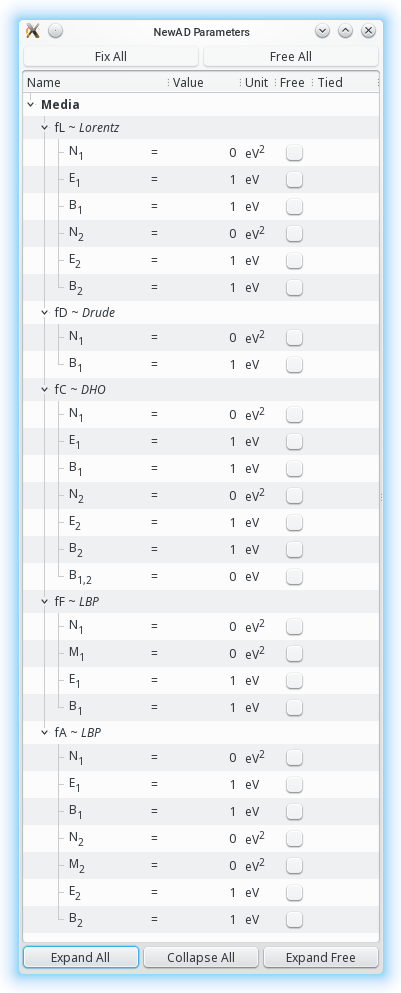
media:
fL = Lorentz:2
fD = Drude
fC = DHO:2
fF = LBP:F
fA = LBP:A:2
newAD2> par
N1fL = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
E1fL = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B1fL = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
N2fL = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
E2fL = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B2fL = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
N1fD = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
B1fD = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
N1fC = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
E1fC = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B1fC = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
N2fC = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
E2fC = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B2fC = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
B1_2fC = 0 fixed (-inf,inf) eV
N1fF = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
M1fF = 0 fixed (-inf,inf) eV2
E1fF = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B1fF = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
N1fA = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
E1fA = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B1fA = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
N2fA = 0 fixed [0,inf) eV2
M2fA = 0 fixed (-inf,inf) eV2
E2fA = 1 fixed [0,inf) eV
B2fA = 1 fixed (0,inf) eV
newAD2>

 |
|